Liquid Helium – Quality & Service – Messer - Specialty Gases
Breadcrumb
Liquid helium
LIQUID HELIUM
The cooling agent to achieve extremely low temperatures, e.g. for MRI or NMR
Nested Applications
Liquid Helium - Introduction 1
Liquid helium – the ultimate coolant for the lowest temperatures and precise applications
Liquid helium, with a boiling point of 4.2 K (−269°C), is the coldest known coolant and is used for numerous applications in the field of low temperatures. Due to its extremely low boiling temperature, it is ideal as a coolant for superconducting magnets and precision analytical instruments. Messer offers liquid helium in Dewar containers with capacities between 50 and 450 liters, as well as in tank containers with volumes of up to 40,000 liters for large consumers such as research institutions and equipment manufacturers. Our experts are available to provide customized advice on the optimal form of supply and the safe handling of liquid helium.
Liquid Helium - Contact Form
Liquid Helium - Introduction 2
Applications of liquid helium in superconductivity and magnetic resonance technology
Most applications of liquid helium focus on superconductivity, which allows materials to be cooled to temperatures below their critical temperature, at which they lose their electrical resistance. This property is crucial for its use in superconducting magnets, which play an essential role in technologies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR).
Nested Applications
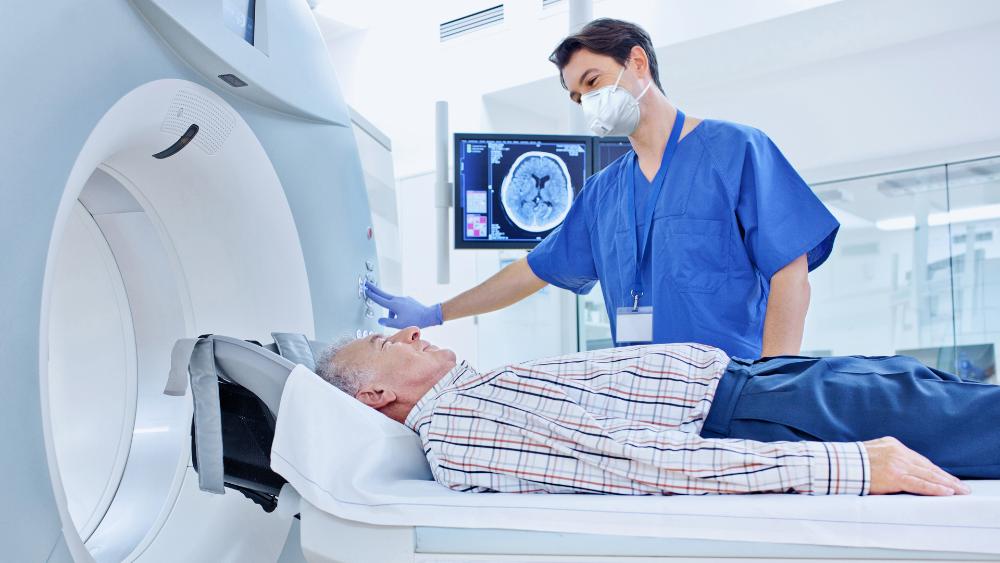
Liquid Helium - MRI
Liquid helium in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), high-intensity magnetic fields are generated, which are are necessary for imaging. These magnetic fields are generated by superconducting magnets, whose magnetic coils must be cooled to temperatures below their critical temperature. Liquid helium performs this function by providing the constant cooling necessary to maintain the superconducting state. Without liquid helium, the operation of these magnets and thus the success of MRI technology would not be possible.
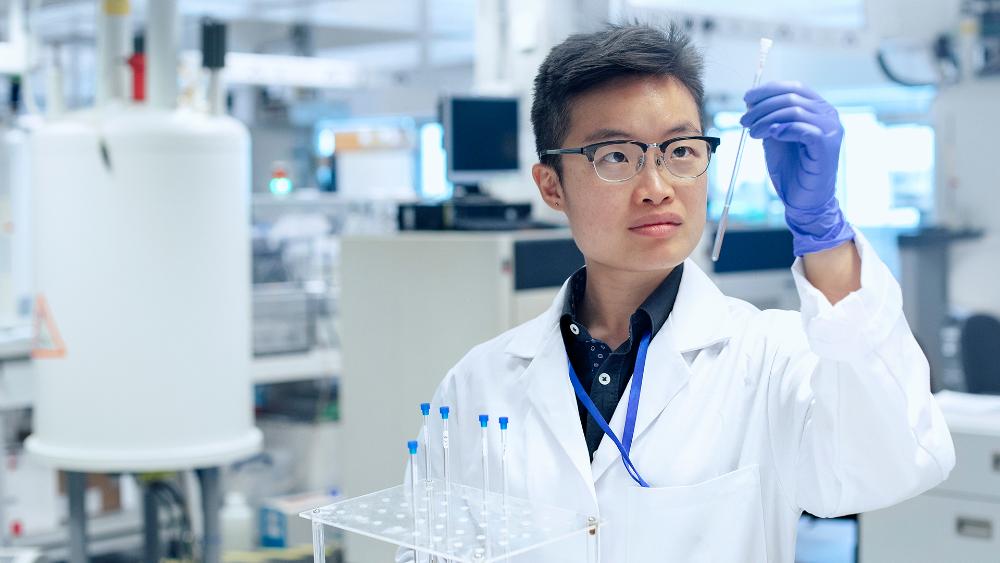
Liquid Helium - NMR
Liquid helium in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR)
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), an important analytical method for determining the molecular structure of substances, strong magnetic fields are required to influence the spin alignment of atomic nuclei. These magnetic fields are generated by superconducting magnetic coils, which must also be cooled to their critical temperature with liquid helium to ensure stable and precise examination of the samples. Therefore, liquid helium is an indispensable coolant in NMR technology.
Nested Applications
Liquid Helium - MRI Image
Liquid Helium - NMR Image

Advantages of liquid helium as a coolant
Advantages of liquid helium as a coolant
Liquid helium offers decisive advantages as a coolant in high-precision applications:
- Extremely low temperatures:
With a boiling point of 4.2 K, it enables cooling to temperatures necessary for superconductivity. - Maintenance of the superconducting state:
Liquid helium ensures constant cooling of superconducting magnets, which is essential for the functional stability and accuracy of systems such as MRI and NMR. - Energy efficiency:
Using liquid helium as a coolant ensures stable and energy-efficient cooling for devices and magnets, keeping them running reliably even over long periods of time.
Buy liquid helium – optimal solutions for your cooling needs
Messer offers liquid helium in various volumes and specifications to meet the requirements of a wide range of applications. Whether for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), or other highly specialized applications, our experts will help you find the optimal solution to operate your equipment efficiently and achieve the desired low temperatures.
Customized consulting and tailored supply options
In addition to supplying liquid helium, we offer comprehensive advice on proper storage, handling, and safe removal. We ensure the smooth and efficient operation of your cooling applications and offer solutions for long-term helium recovery.
For customized quotes and comprehensive advice on the safe use of liquid helium, please contact us at any time.
Specialty gase page
SPECIALTY GASES
Do you have high standards? We do, too. Specialty gases from Messer
Contact form for every page
Contact us
select action


